Arbolaria Tropical Project
See also, the project website: Arbolaria Tropical (in both English and Español).
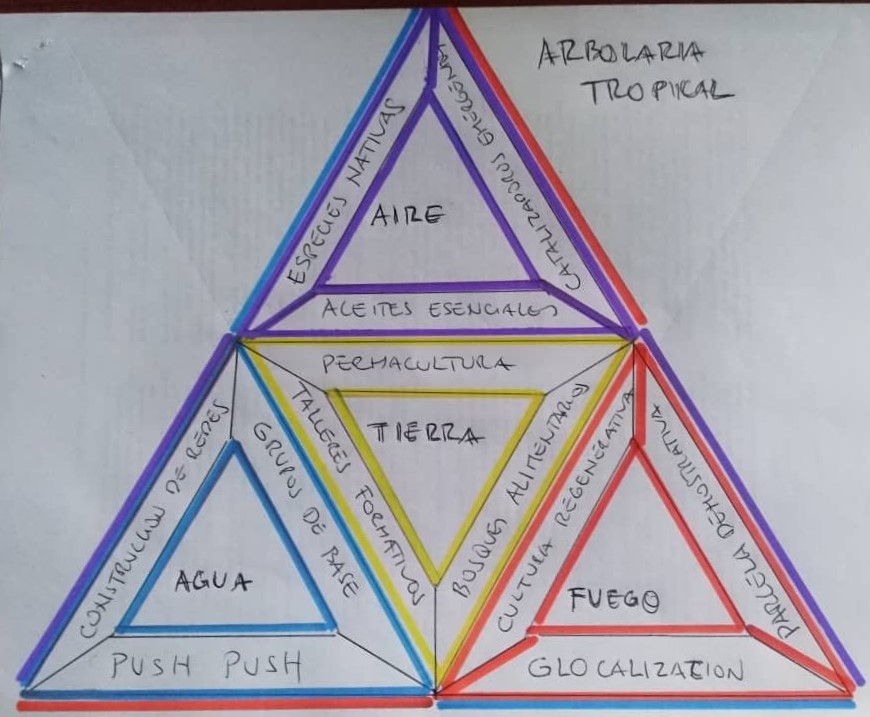
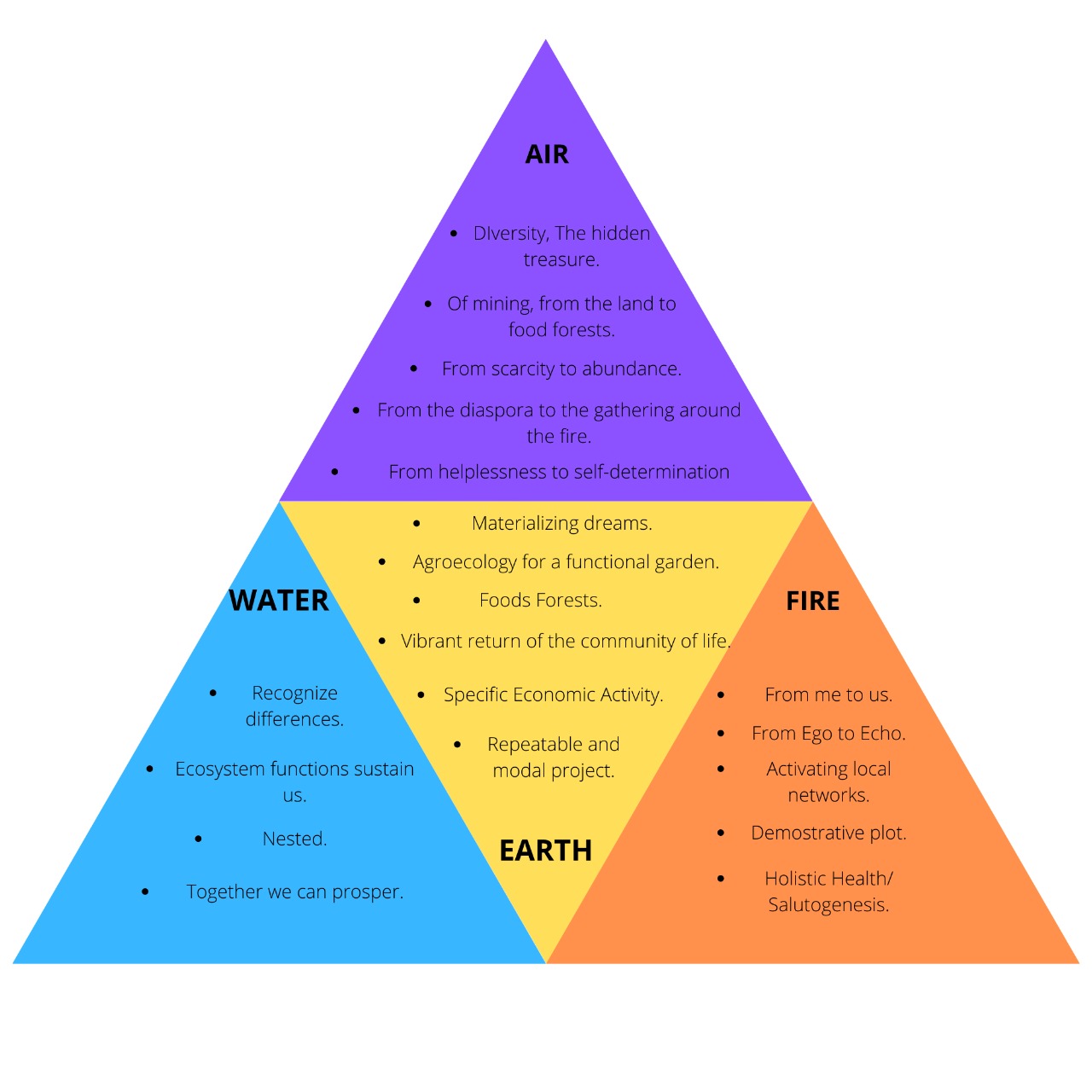
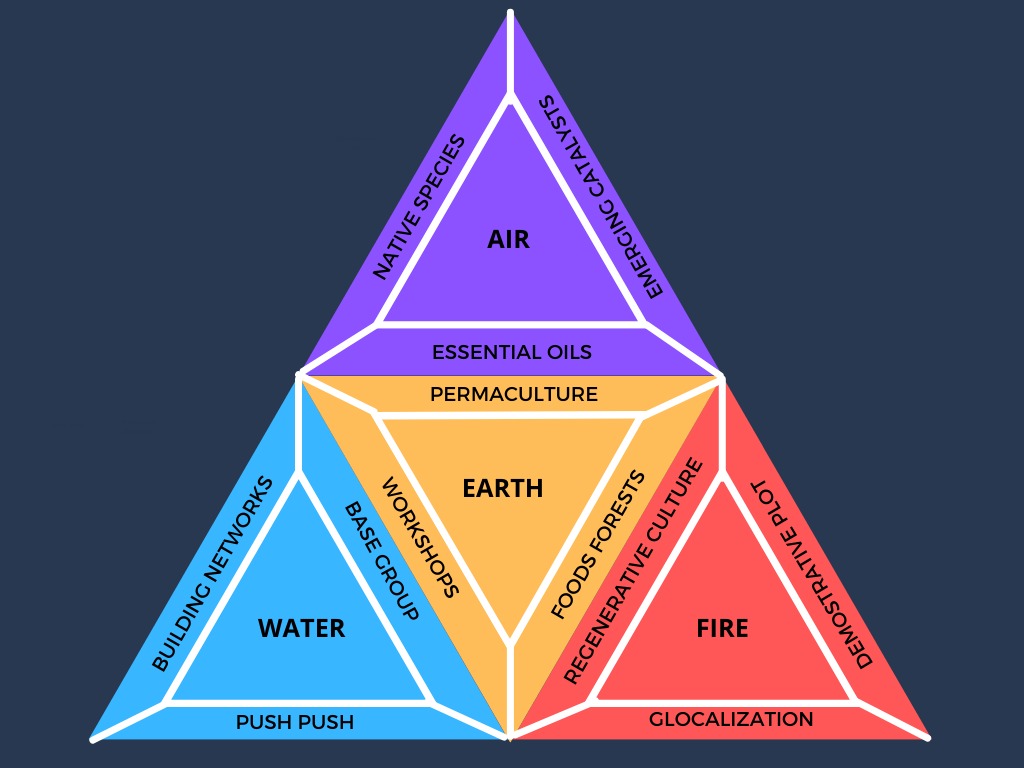
Our goal is the production of high purity vegetable oils for cosmetic, aesthetic, culinary, aromatic and medicinal use made from high quality raw materials. These raw materials are obtained from sustainable agroforestry crops and local food forests which allow the regeneration of deteriorated natural ecosystems, leading to the preservation of biodiversity and restoring the social fabric of the rural communities involved.
|
|
 |
| Elements | Relationships |
 |
 |
|
EXPLICIT
|
IMPLICIT
|
|
Social Context |
Social Potential |
| Communities on the edge of urban and rural areas. Local communities with Little expertise in agricultural work, little academic training, high dependence on state aid. Fragile social fabric due to migration and marginalization. The local inhabitants do not own the land, the community of agro-producers are the owners of the land, but the vast majority live in the city. Impoverished middle class in recent years. Acceptable academic and professional training, growing interest in the innovation of appropriate and sustainable agricultural technologies and willing to tackle problems of environmental deterioration. | Empowered local communities as agents of positive change in the bioregion. Trained in the creation and maintenance of family and community gardens and food forests. Managing your direct access to healthy, diverse and abundant food. Boosting family and cooperative ventures by participating in the value chain. Permaculture training. Access to sustainable technologies such as water harvesting, dry toilets, biodigesters and bio-construction. Community of agro-producers committed to the local community and the ecosystem, participating in collaborative and cooperative strategies. |
| Environmental Context | Environmental Potential |
| Damaged ecosystems, loss of soil fertility (conventional agricultural production systems, use of chemical agents, plowing machinery), difficult access to water, lost surface aquifers, underground aquifers more than 40 m deep. Compromised biodiversity, loss of historical habitats due to the expansion of agricultural frontiers, cutting and burning of forests. | Restoration of native ecosystems, regeneration of degraded areas from sustainable ecological systems such as permaculture, agroforestry, key line system, reforestation practices and recovery of watersheds, recovery of habitats capable of promoting biodiversity. |
| Economic Context | Economic Potential |
| Impoverished local communities, income of less than US $ 1 per day from informal work (commerce). Great basic needs, ranches without aqueduct or sewage, dirt floors. No productive undertaking. Community of agricultural producers with little capacity to manage enterprises due to the collapse the nation is facing, little access to financing. Agro-productive systems in decline. | The choice of a range of plant species that allow the extraction of vegetable oils with demand in the national and global market. The construction of a value chain, agricultural production, transformation of raw materials and commercialization, allowing the creation of work on a personal, family, community, cooperative scale and the revitalization of the local economy. |
| Political Context | Political Potential |
| Central and institutional government with scarce and insufficient presence, local governments in formation (Communal Councils and Communes) of limited scope and organization. | Formulation of Governance agreements, empowerment of community activities. Self-management. |
